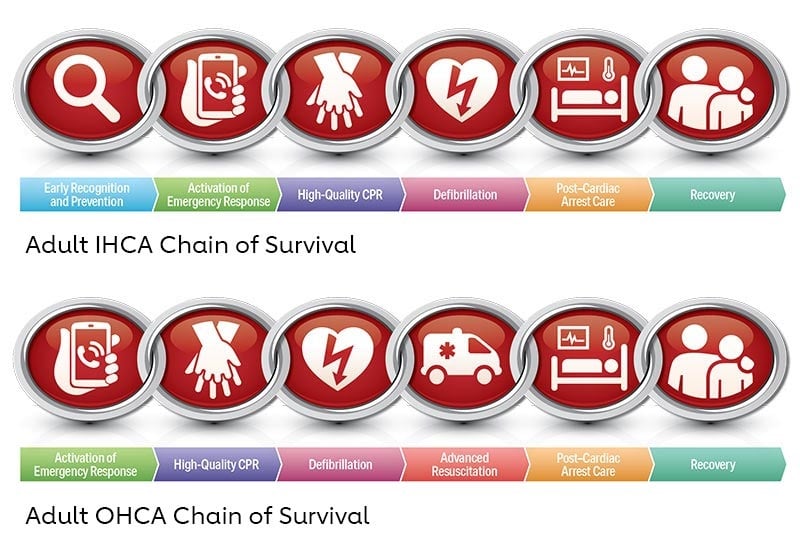
The ACLS (Advanced Cardiac Life Support) algorithm for cardiac arrest outlines a structured approach to resuscitation efforts. The algorithm aims to restore normal cardiac function. It begins with the immediate assessment of the patient’s responsiveness and breathing. If the patient is unresponsive, CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) is initiated immediately. High-quality chest compressions and adequate ventilation are also needed.
The ACLS algorithm protocol for cardiac arrest focuses on the importance of early defibrillation for shockable rhythms. Defibrillation is followed by rapid administration of medications like epinephrine and antiarrhythmics, along with ongoing CPR cycles.
Continue reading and find a complete breakdown of the ACLS algorithm protocol.
How does an ACLS algorithm for cardiac arrest work?
In the critical moments following cardiac arrest, a structured and systematic approach can make all the difference in saving lives. The Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) algorithm guides healthcare providers by offering a step-by-step roadmap. Here’s how the ACLS algorithm for cardiac arrest works:
- Assessment and Recognition: Healthcare providers immediately assess the patient’s responsiveness and breathing. If the patient is unresponsive and not breathing, cardiac arrest is recognized, and CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) is initiated.
- CPR Initiation: High-quality chest compressions and adequate ventilation are initiated. This ensures circulation and oxygenation to vital organs.
- Defibrillation: For shockable rhythms such as ventricular fibrillation (VF) or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT), early defibrillation is important. Healthcare providers deliver a shock using a defibrillator as soon as possible. However for non shockable rhythms, defibrillators hold no value.
- Medication Administration: After defibrillation, rapid administration of medications such as epinephrine and antiarrhythmics is initiated. These medicines restore and maintain a stable cardiac rhythm.
- Advanced Interventions: Advanced airway management techniques like endotracheal intubation or supraglottic airway placement can be administered. Additionally, targeted temperature management can be initiated for post-cardiac arrest care. This eliminates the chances of neurological damage.
- Effective Team Dynamics: Throughout the resuscitation process, effective communication and coordination within the healthcare team are essential. Roles and responsibilities are clearly defined to ensure smooth execution of resuscitation efforts.
- Continual Assessment: Healthcare providers continually reassess the patient’s response to interventions, adjusting treatment strategies as necessary based on the patient’s condition and response.
By following the ACLS algorithm for cardiac arrest, healthcare providers can navigate through the complexities of resuscitation with confidence and precision, maximizing the chances of successful outcomes for patients in need.
Key benefits of an ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
ACLS (Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support) Cardiac Arrest algorithm helps healthcare professionals navigate through the intricacies of cardiac disorders. Below mentioned are the key benefits of ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm.
- Structured Approach: The ACLS cardiac arrest algorithm provides a systematic and organized framework for healthcare providers to follow during resuscitation efforts, ensuring that critical steps are taken promptly and effectively.
- Clear Guidelines: This algorithm offers clear and concise guidelines for assessing and managing cardiac arrest. This includes protocols for initiating CPR, administering medications, and delivering defibrillation.
- Improved Outcomes: By following the ACLS algorithm, healthcare providers can optimize the delivery of interventions. This leads to improved patient outcomes and increased survival rates post cardiac arrest.
- Standardization: This algorithm promotes consistency and standardization in cardiac arrest management. This allows for seamless coordination and communication among healthcare providers.
- Adaptability: While providing a structured framework, the ACLS algorithm also allows for flexibility and adaptation based on the specific needs of the patient and the clinical context, ensuring that interventions are tailored to individual circumstances.
- Training and Education: Algorithms serve as a valuable educational tool for healthcare providers. This facilitates training and skill acquisition and helps implementing the best practices in critical interventions.
- Quality Assurance: By incorporating evidence-based guidelines and best practices, the ACLS cardiac arrest algorithm supports quality assurance initiatives within healthcare organizations, promoting adherence to standards of care and continuous improvement in resuscitation outcomes.
What are the cardiac disorders addressed by an ACLS cardiac arrest algorithm?
The ACLS cardiac arrest algorithm guides healthcare providers through the management of various cardiac disorders. Here are the cardiac disorders addressed by the ACLS algorithm:
- Ventricular Fibrillation (VF): A chaotic, rapid, and disorganized electrical activity in the heart, resulting in ineffective contractions and cardiac arrest.
- Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): A rapid heart rhythm originating from the ventricles, leading to inadequate blood flow and cardiac arrest.
- Asystole: Complete absence of electrical activity in the heart, resulting in the absence of a pulse and cardiac arrest.
- Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA): Electrical activity present on the electrocardiogram (ECG) without effective mechanical contractions of the heart, leading to cardiac arrest.
- Bradycardia: Abnormally slow heart rate, which can lead to inadequate perfusion and cardiac arrest if not corrected.
- Tachycardia with a Pulse: Rapid heart rate with a pulse, which may require intervention to prevent progression to more severe arrhythmias or cardiac arrest.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ACLS cardiac arrest algorithm serves as a vital lifeline in the management of various cardiac disorders. From ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia to asystole and bradycardia, this algorithm provides healthcare providers with clear protocols and interventions. The ACLS algorithm protocol for cardiac arrest motivates healthcare providers to navigate through the complexities of cardiac emergencies, which ultimately saves lives and preserves health.